Hand, foot and mouth disease or shortly known as HFMD is a disease that is caused by the Coxsackievirus and Enteroviruses.
HFMD is highly contagious and can affect both children and adults. However, children under the age of 5 are more exposed to this virus.
You can get infected by this virus through direct contact with unwashed hands or surfaced areas that are contaminated with faeces.
You are also exposed to this virus if you are in contact with an infected person’s saliva, blisters, tools or respiratory secretions.
How do I know if it is HFMD?
- You have a fever, sore throat and headache.
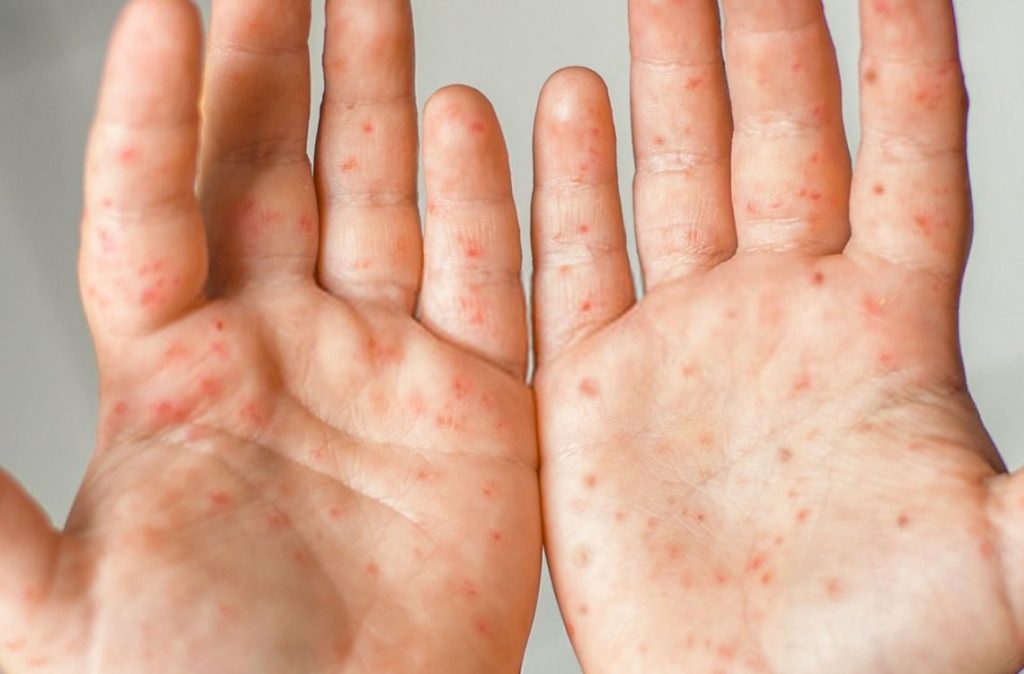
- Red spots start to develop on your palms and soles. These red spots are not itchy.
- You will also have blisters or sores in the mouth and rashes on the hands and feet.
- The infected person will also have a poor appetite and irritability.
What are the treatments for HFMD patients?
HFMD would go away without treatment in 7 to 10 days after our bodies immunity has developed. There is no specific medication that can kill the virus.
Doctors will also cure it according to your child’s symptoms. For example:
- Prescription or over-the-counter topical ointments to soothe blisters and rashes.
- Pain medication to relieve headaches.
- Medicated syrups or lozenge that can ease painful sore throats.
The Ways to Prevent HFMD From Spreading
At the moment, there are no specific vaccines or medication to prevent HFMD but it is important to lower the risk of getting it by doing these:
- Practice good hygiene.
- Teach your children to wash their hands regularly.
- Disinfect any common areas that are always touched by the family.
- Cover nose and mouth when sneezing.
- Don’t share cups or utensils with infected people.
- Don’t send your infected child to school or daycare until their symptoms are gone. Check with your doctor if you think they might still be contagious. Usually, it is highly contagious during the first week of the disease.
Possible Complications of HFMD
Although the disease usually will go away after seven days, it can cause some complications such as:
- DEHYDRATION – this happens when your child refuses to drink water because of the mouth sores.
- SWELLING – the swelling of the membranes around the brain, spinal cord and heart muscles.
- ENCEPHALITIS – a severe and potentially life-threatening disease involves brain inflammation caused by a virus. This complication is rare.
HFMD is NOT the same as Foot-and-Mouth Disease
One thing to take note is that HFMD and foot-and-mouth disease is different! Foot-and-mouth or also called hoof-and-mouth disease affects animals such as cattle, sheep, and swine.
Despite that this virus usually have mild cases and it is nowhere near the COVID-19, it does not mean that we, as parents, should take it lightly.
Remember that prevention is better than cure. Don’t regret it before it is too late.
Make sure to always wash your hands and sanitise common places that everyone touches. Wear a mask if you are feeling sick.